MASTER OF SCIENCE IN ARCHITECTURE SPRING 2021
GRADUATE RESEARCH DESIGN STUDIO I
Diana Agrest, The Irwin S. Chanin Distringuished Professor
The Body: Corporeal Boundaries and Spatial Intersections
The subject of the body has deep roots in Western architecture theories from the texts of the Renaissance reading of Vitruvius. From Alberti to Francesco di Giorgio Martino and Filarete, the body has been a referent, a tool, and a construction in which the body (of man) is both a metaphoric and a metonymic construction having perfect proportions and harmony based on nature in whole and in part. This embodiment of nature, thus God, is consistent with the transfer of the center from God to man. We can fast-forward to the culture of disembodiment brought about as a result of cybernetics, information, mediatization, and in general, virtual reality, in a world that is nothing but simulacrum and in which the body becomes, in its many forms of representation, a simulacrum itself.
In the long stretch in between there are all forms of architectural constructions of the body, from the Ernst Neufert's Architects’ Data of 1936 to The Modulor by Le Corbusier of 1945 and 1955, or the implied control of the body in the earlier Radiant City of 1930 through the question of healthy bodies through sun, air, and open space. One could certainly say a lot about these narratives of control of the body in space as they relate to the body as a machine in a prevailing technocratic ideology, and the body as a tool for consumption and control of the space of habitation. But while these are meant to be social tools, one could still ask What body is the body in question?
And then there is the question of the places and spaces affected by and/or affecting the body and modes of control such as the institutions famously studied by Michel Foucault in History of Madness, Discipline and Punish: The Birth of the Prison, and The History of Sexuality. Or one could look at the body, in its corporeality and the pushing of the limits of the body itself, as in athletic activities and competitive sports, becoming at once actors being the subject of the spectacle, as in the Olympics, rock climbing, or cave explorations. Or the overcoming of its boundaries through the means of possible extensions, from those related to the senses, to parts of the entire body through the possibilities afforded by constantly changing and advancing technologies that have gone from the mechanical to the digital. This includes all forms of prosthetic devices, some remedial and some just expansive per se becoming actually cyborgs, as Haraway so vividly prognosticated. Or the body relative to the myriad organisms that interact and affect it from within and from without as the body relates to questions under the general rubric of health and the many different modes in which health and the overcoming of disease and the body/machine interaction are once more enacted.
But again, what body? The question is that of difference as opposed to the universalization of an abstract (male) body. Differences of all kinds—from genetic to cultural, including questions of sex, gender, race, or ethnicity, including the labeling of bodies, but which in fact touch on the most profound forces that travel through fluids and synapses traversing the whole body in billions of possible routes, rhythms and outcomes, each unique, including transformation of the body in the process of reproduction.
But this body is affected if not completely determined by socio-political, economic, cultural, ideological, and physical environments and enacted in diverse places and modes habitation, from the physical body to a culture of disembodiment in the cyberspace we inhabit, which is exacerbated at present. This brings us back to questions of what bodies are we talking about and where are these bodies and how are those boundaries and spatial intersections enacted?
This studio articulates the issues of bodies in their articulations and intersecting boundaries from a critical perspective. This exploration was developed in specific contexts in which students discovered their own individual interests. The project will address both the body itself and the environments where they operate as a creative and seamless process with no separation between research and project. The studio also emphasizes the importance of drawing as essential to this creative process.
Projects
-
Cyborg: An Artificial Sensorial Sublime
-

Body and Taoist Philosophy—Life Energy and Movement
-
The Manifestation of the Female Body in a Male-Dominated Sport: Ski Jumping
Back
Cyborg: An Artificial Sensorial Sublime
Foivos Geralis
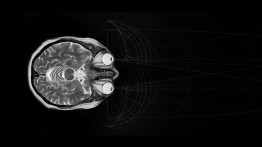
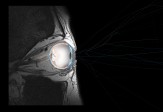
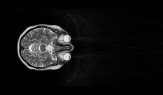
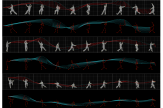
Since the beginning of the pandemic we have witnessed a radical transformation of our quotidian lives. Zoom, computer screens, mobile screens, television sets—all mediating the world, transforming everyday life in a way that can be traced back to the first literary depictions of cyborgs and the technotopias of the collective, aesthetic unconscious of the ‘60s and ‘70s, and the emergence of cybernetics in science and pop culture. But traces of the idea of cyborgs can be found long before that. Cyborgs, accentuating and prioritizing vision over the other senses, begin with the invention of the cyborg theory, from Norbert Wiener and Marshall McLuhan’s view of technologies as extensions of the human body, to today’s incorporation of those technologies as an imperative supplement to the human body in what I call medical cyborgs. Of course this has been accentuated by all the external devices that have materialized in the last decades—monitors, phones, smart watches, the internet, satellite imaging, etc.—all of which constitute a new type of normalcy provided only through the use of these technologies.
Recent medical developments with experimental retinal transplants are using digital technologies to restore vision to blind people. This is a decisive step forward in the technologies augmenting human vision. The insertion of a digitally controlled optical lens and electronically stimulated optical nerves is fundamentally different from the simple lens replacement now regularly used to ‘fix’ cataracts or myopia. That is because it is not a passive medium, but an interactive electronic device permanently implanted in the human body.
This project studies sensorial perception as a holistic experience that transcends the limitations of the visual. By experimenting with the expansion of spatial boundaries via manipulated visual and auditory environments, I aim to reveal a corporeal effect—one of a subject facing the sublime.
Body and Taoist Philosophy—Life Energy and Movement
Tao He
Taoist philosophy is a tradition of Chinese origin that emphasizes living in harmony with the Tao, which means “the Way.” In Chinese philosophical contexts, Tao is understood to be the highest conceivable principle, the “supreme ultimate.” Wudang, the most important representative genre of Chinese Taoism, is located on Wudang Mountain, home to a famous complex of Taoist temples and monasteries. Wudang is renowned for the practice of the Taoist philosophy, and Taoist priests reside permanently in Wudang Mountain to pursue Taoism.
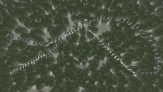
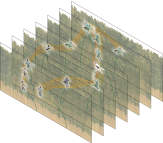
My project studies the body in the enactment of Wudang Sword. Wudang Sword, originating from the Wudang genre, is a body of Chinese straight sword techniques encompassed by internal martial arts. Wudang Sword is the most important physical practice and a compulsory course for priests pursuing Taoism. Wudang Sword is based on Taoist philosophy, specifically the principles of Yin and Yang and Ch'i—"life energy"—devoted to internal energetic and physical training. The practice of Wudang Sword is understood as the physical expression of Taoist principles from which tranquility and movement are expressed, body and existence flow, and the Yin and Yang originate, alternately becoming each other’s source.
My methodology for this project began with a general approach to the enactment of Wudang Sword that mainly focused on the movement of both body and sword—the extension and contraction of the body, and the flow of the sword’s movement. I then specifically focused on the body’s movement, life energy, and Taoist philosophy of the Wudang Sword through the narrative of classic martial arts film Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon in which Princess Yu, in particular, combines elements of Wudang Sword and Taoist philosophy. Princess Yu’s personal evolution and life experience with the sword depicts tensions between male and female, oppression and resistance, and a struggle to pursue love and freedom independently, all of which echo the core spirit of Taoist philosophy.
The Manifestation of the Female Body in a Male-Dominated Sport: Ski Jumping
Sophie Krauss
My interest in the winter sport of skiing leads back to my personal experience with it: my family spent the winter season in the mountains to pursue skiing, our biggest hobby. But a closer look into the professional world of skiing reveals a very male-dominated sport.
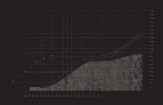
This project explores the sport of ski jumping and its general exclusion of the female body. Ski jumping has its origins in Norway—the first measured jump occurred in 1809 when a Norwegian lieutenant, Olaf Rye, jumped almost 9.5 meters through the air to prove his courage to his soldiers. This early example illustrates how deeply rooted the male body is in the sport. Over two hundred years later, gender politics haven’t much changed in the sport. Women are still a small minority and face huge differences in income and participation in international competitions like the Olympics. Ski jumping has been part of the Olympics since its founding in 1924 in Chamonix, France, but it took ninety years—until 2014—for the first women to officially compete. The biggest ramps, which are also the most celebrated, are still reserved for male jumpers.
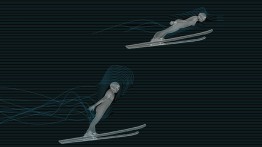
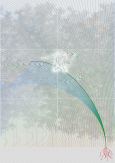
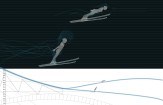
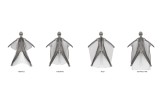
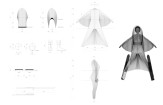
My project evolved to focus on a common sport that combines flying and skiing, realized through new designs for wingsuits. There are currently no wingsuits to address this, so I designed one for women. While the wearer is skiing she should have flexibility in her arm and leg movement, so my wingsuit is designed to adjust to accommodate this. While she’s flying, she should have wings located between her upper body and arms, as well as between her legs, which helps her glide. My personal experience with skiing prompted me to design a hood above the wearer’s head, which improves safety and also protects against rain and wind.
For the last part of my project I created a choreography for the wingsuit in Garmisch Partenkirchen, in southern Germany, that starts at the Zugspitze—the highest mountain in Germany—and ends at Alpspitze mountain. The choreography begins with skiing and transitions to flight.